How to cure stroke (part 2)
The need for redistribution of blood between the different areas of the brain occurs both in physiological conditions, enhancing the functional activity, as in pathology caused by stenosis or obturation of vascular lumen. In such kind of situations it is significant and crucial role of collateral circulation (CC) to be taken into account. A rich network of anastomoses between arteries, carrying out blood and brain (between the front, middle and posterior cerebral arteries between the carotid and vertebro-basilar basin through the circle of Willis vessels) makes opportunities of blood redistribution between the different areas and compensation for reduced blood flow. Of course, the rate of incorporation of QA is essential for the effective implementation of cerebral blood flow. The high sensitivity of ganglion nerve cells of the brain to the factor hypoxia-ischemia causes a short time period is the restoration of blood flow through the rapid expansion of collateral vessels.
The delay of QA leads to the formation of focal ischemia with loss of brain tissue. Possibility of adequate QA depends primarily on the rate of occlusion of the lumen of the vessel. Thus, with a high rate of development of blockage of the vessel (eg, embolism), there is usually focal symptoms, on the contrary, the slow closing of the lumen of the artery and, therefore, well-developed collateral circulation, clinical symptoms may be transient in nature. Important to ensure the spacecraft are systemic blood pressure levels, the preservation of metabolic and myogenic mechanisms of self-regulation of cerebral circulation, especially individual cerebral vessels architectonics, level of obturation of the vascular lumen (main vessels of the head, the main arterial trunks or smaller vascular branches). Any damage to the individual branches of the proximal aortic arch (nameless and common carotid arteries, subclavian artery) may occur “steal syndrome” at the expense of cerebral blood flow, accompanied by cerebral symptoms.
Features vascular compensation are very important. Suffice it to recall that the literature describes the cases of complete closure (thrombosis) of one, two or even three of the great arteries with minor clinical symptoms, in which patients retain the ability to work. When incomplete compensation of regional cerebral blood flow arise initial clinical symptoms of cerebral circulation insufficiency.
The concept of cerebral vascular insufficiency is generally defined as a state of imbalance between demand and delivery of blood to the brain. It is based, most often, the restriction of blood flow in atherosclerotic narrowed brain vessels. This temporary decrease in systemic blood pressure can cause the development of ischemic brain region supplied by a vessel with a narrowed lumen. Atherosclerotic stenoses are beginning to show clinical symptoms only in their luminal narrowing of more than 50%. The potential inadequacy of blood supply of the brain due to cerebral vascular sclerosis usually manifests clinically with a further reduction in blood flow, in particular, with a decrease in blood pressure (myocardial infarction, the weakness of left ventricular function), incidence of vascular tone during shock or collapse, with a decrease or redistribution of the mass of blood (blood loss , diversion of blood to the periphery in the hot, radiation), diseases that lead to cerebral hypoxia (blood disease, pulmonary insufficiency, intoxication). All these reasons can lead to cerebral vascular nedostatochnocti and development of transient or persistent violations of the functions of the brain.
Epidemiological studies have shown the role and importance in the development of vascular pathology of the brain called risk factors, ie such features of the environment or the organism itself, which increases the risk of disease. The main risk factors include: age over 40 years of hereditary family history, obesity (often accompanied by hypercholesterolemia), lack of physical activity and psycho-emotional strain, smoking and regular alcohol consumption, nutritional factors (excessive consumption of animal fat, salt).
Indisputable risk factor is diabetes, boost the development of atherosclerosis. It is important that even a slight increase in blood sugar contributes to increasing the frequency of strokes.
A leading role has increased in AD. It is well known that patients with arterial hypertension strokes occur much more frequently than the “normotensive”. Systemic treatment and a persistent reduction in blood pressure significantly reduces the risk of cerebral lesions.
Some importance are persistent cardiac arrhythmia, particularly atrial fibrillation in the elderly, heart valve defects, chronic thrombophlebitis, blood disorders (erythremia, various leukemias). In the elderly are emerging as factors such as insolation, hot tubs, a tendency to constipation, as well as postoperative bleeding with a fall in blood pressure.
Modern classification of disorders of cerebral circulation divides them into two groups:
- Chronic disorders of cerebral circulation during encephalopathy – discirculatory genesis of hypertensive encephalopathy and atherosclerotic discirculatory encephalopathy.
- Acute disorders of cerebral circulation – a hemorrhagic stroke, ischemic stroke (cerebral infarction), transient disorders of cerebral circulation.
Transient disorders of cerebral circulation – is acutely emerging NMC, showing focal or general cerebral symptoms and lasting no more than 24 hours (according to WHO classification). In the foreign literature they are often called transient ischemic attacks, as the basis of their usual lies transient ischemia in the basin of a cerebral vessel.
In contrast to the transient disorders of cerebral circulation strokes are characterized by persistent violations of brain functions, expressed in varying degrees. By the nature of the pathological process of stroke is divided into two large groups – hemorrhagic and ischemic.
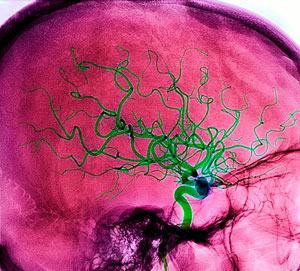
In the WHO rates of stroke varies from 1,5 to 7,4 per 1000 population, growing with age. Highest-incidence between the ages of 50 and 70 years. Thus, at the age of 50-59 years, incidence of stroke is equal to 7.4, and those aged 60-69 years – 20 per 1000 population. Over the past four decades has changed the structure of vascular diseases of the brain due to the predominance of ischemic stroke over hemorrhagic.
Posted in Head and Brain